This works well for vehicles, equipment, and other physical assets, but it cannot be used for intangible assets. The General Depreciation System (GDS) is the most common method for calculating MACRS. If you own a building contribution margin that you use to make income, you can claim the depreciation on this property.

Recording Depreciation, Depletion, and Amortization (DD&A)
If the depreciation deductions for your automobile are reduced under the passenger automobile limits, you will have unrecovered basis in your automobile at the end of the recovery period. If you continue to use the automobile for business, you can deduct that unrecovered basis after the recovery period ends. You can claim a depreciation deduction in each succeeding tax year until you recover your full basis in the car. The maximum amount you can deduct each year is determined by the date you placed the car in service and your business/investment-use percentage.
- You stop depreciating property either when you have fully recovered your cost or other basis or when you retire it from service, whichever happens first.
- Depreciation is a standard accounting method that lets businesses divide the upfront cost of physical assets—from delivery trucks to data centers—across the number of years they expect to use them.
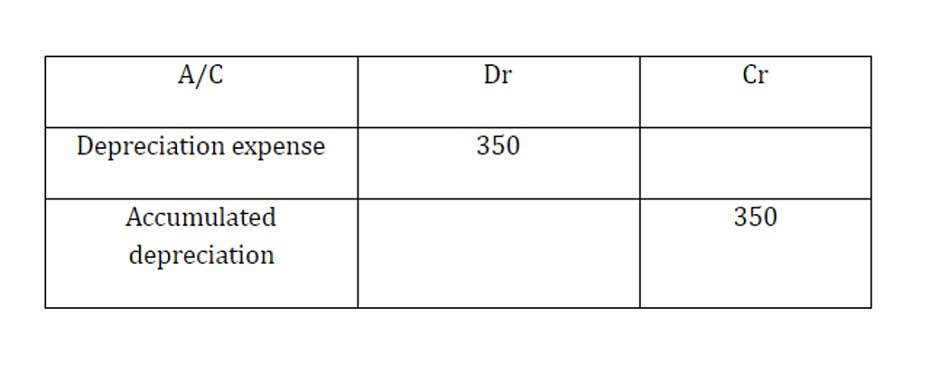
- So to calculate the depreciation expense, we need to quantify the useful life of the asset mathematically.
- One of the main financial statements (along with the statement of comprehensive income, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and statement of stockholders’ equity).
- If you and your spouse elect to amend your separate returns by filing a joint return after the due date for filing your return, the dollar limit on the joint return is the lesser of the following amounts.
- This is an owner’s equity account and as such you would expect a credit balance.
How can Taxfyle help?
- As explained earlier under Which Depreciation System (GDS or ADS) Applies, you can elect to use ADS even though your property may come under GDS.
- For example, when Microsoft invests $80 billion in AI infrastructure, it will deduct portions of those purchases each year, lowering its corporate tax bill.
- You can elect the section 179 deduction instead of recovering the cost by taking depreciation deductions.
- The double-declining-balance (DDB) method, which is also referred to as the 200%-declining-balance method, is one of the accelerated methods of depreciation.
- Property with a long production period and certain aircraft placed in service after December 31, 2023, and before January 1, 2025, is eligible for a special depreciation allowance of 80% of the depreciable basis of the property.
- To calculate depreciation on real estate, you first have to know the cost basis.
However, if you drive a car for work and for personal use, you can only claim depreciation on the business portion of your tax return (for example 60% of the cost). Understanding depreciation is important for getting the most out of your assets at tax time. You can claim depreciation to reduce your total taxable income, saving you money on your taxes. For example, a commercial building has a useful life of 39 years, while machinery often has a shorter lifespan and higher depreciation using accelerated methods like the declining balance method.

How To Easily Track Depreciation
- This helps you track where you are in the depreciation process and how much of the asset’s value remains.
- You multiply the adjusted basis of the property ($1,000) by the 40% DB rate.
- A depreciable asset is property that provides an economic benefit for more than one reporting period.
- XYZ’s taxable income figured without the section 179 deduction or the deduction for charitable contributions is $1,240,000.
For business aircraft, allocate the use based on mileage or hours on a per-passenger basis for the year. This can be done using the flight-by-flight method or the occupied-seat method computations. A qualified moving van is any truck or van used by a professional moving company for moving household or business goods if the following requirements are met.
Your spouse has a separate business, and bought and placed in service $300,000 of qualified business equipment. This is because you and your spouse must figure the limit as if you were one depreciable assets taxpayer. You reduce the $1,220,000 dollar limit by the $300,000 excess of your costs over $3,050,000.


Tools like lease accounting software or asset management platforms can simplify this process and ensure Grocery Store Accounting compliance. Proper asset classification is crucial for accurate financial reporting and tax efficiency. By categorizing assets correctly, you ensure compliance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and optimize your depreciation deductions. Depreciation allows you to allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life, spreading the deduction across multiple accounting periods. This reduces taxable income and ensures compliance with accounting standards like GAAP and international financial reporting standards (IFRS).
After you figure your special depreciation allowance for your qualified property, you can use the remaining cost to figure your regular MACRS depreciation deduction (discussed in chapter 4). Therefore, you must reduce the depreciable basis of the property by the special depreciation allowance before figuring your regular MACRS depreciation deduction. Thus, the amount of any 2024 disallowed section 179 expense deduction attributable to qualified section 179 real property will be reported on line 13 of Form 4562. This disallowed deduction amount is shown on line 13 of Form 4562.

What Property Does Not Qualify?
Like-kind exchanges beginning after December 31, 2017, are generally limited to exchanges of real property not held primarily for sale. Section 1.168(i)-6 of the regulations does not reflect this change in law.. If you have two or more successive leases that are part of the same transaction (or a series of related transactions) for the same or substantially similar property, treat them as one lease. A special rule for the inclusion amount applies if the lease term is less than 1 year and you do not use the property predominantly (more than 50%) for qualified business use. The amount included in income is the inclusion amount (figured as described in the preceding discussions) multiplied by a fraction. The numerator of the fraction is the number of days in the lease term, and the denominator is 365 (or 366 for leap years).




 English
English